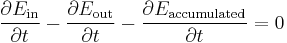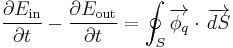Heat flux
Heat flux or thermal flux is the rate of heat energy transfer through a given surface. The SI derived unit of heat rate is joule per second, or watt. Heat flux is the heat rate per unit area. In SI units, heat flux is measured in [W/m2][1]. Heat rate is a scalar quantity, while heat flux is a vectorial quantity. To define the heat flux at a certain point in space, one takes the limiting case where the size of the surface becomes infinitesimally small.
Heat flux is often denoted 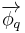 , the subscript q specifying heat rate, as opposed to mass or momentum rate. Fourier's law is an imporant application of these concepts.
, the subscript q specifying heat rate, as opposed to mass or momentum rate. Fourier's law is an imporant application of these concepts.
Measuring heat flux
The measurement of heat flux is most often done by measuring a temperature difference over a piece of material with known thermal conductivity. This method is analogous to a standard way to measure an electric current, where one measures the voltage drop over a known resistor.
Relevance to science and engineering
One of the tools in a scientist's or engineer's toolbox is the energy balance. Such a balance can be set up for any physical system, from chemical reactors to living organisms, and generally takes the following form
where the three 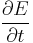 terms stand for the time rate of change of respectively the total amount of incoming energy, the total amount of outgoing energy and the total amount of accumulated energy.
terms stand for the time rate of change of respectively the total amount of incoming energy, the total amount of outgoing energy and the total amount of accumulated energy.
Now, if the only way the system exchanges energy with its surroundings is through heat transfer, the heat rate can be used to calculate the energy balance, since
where we have integrated the heat flux density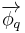 over the surface
over the surface 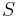 of the system.
of the system.
In real-world applications one cannot know the exact heat flux at every point on the surface, but approximation schemes can be used to calculate the integral, for example Monte Carlo integration.
See also
- Eddy covariance flux (eddy correlation, eddy flux)
- Heat Notation
- Heat conduction
- Heat transfer
- Critical heat flux
- Latent heat flux
- Rate of heat flow
- Insolation
- Heat flux sensor
- Relativistic heat conduction
- ^ The NIST Reference on Constants, Units, and Uncertainty http://physics.nist.gov/cuu/Units/units.html